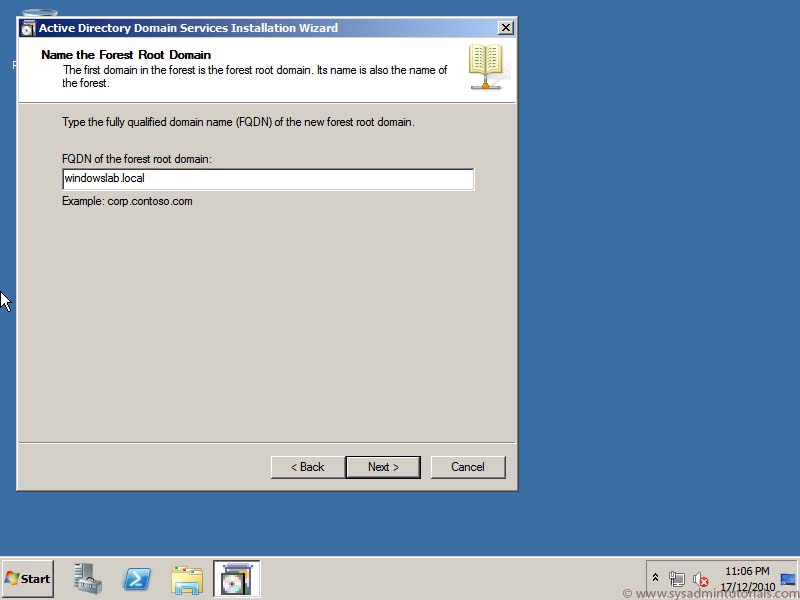
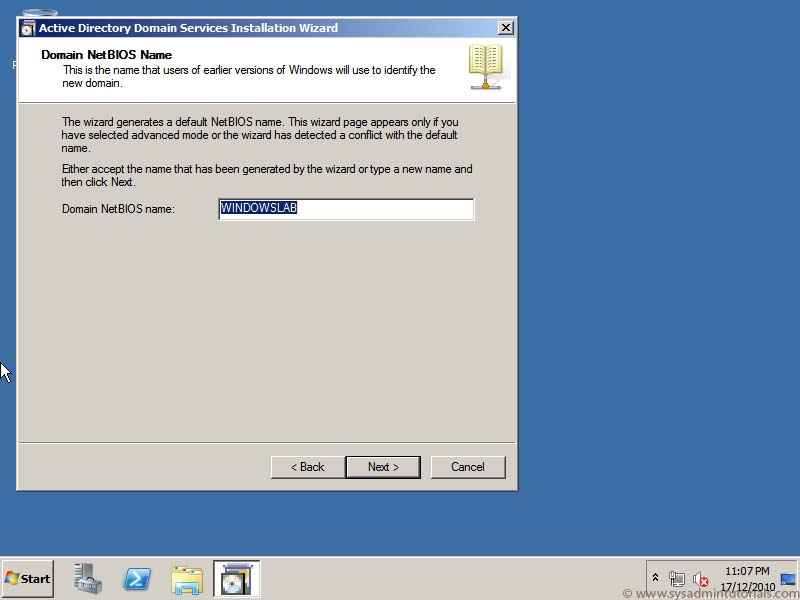
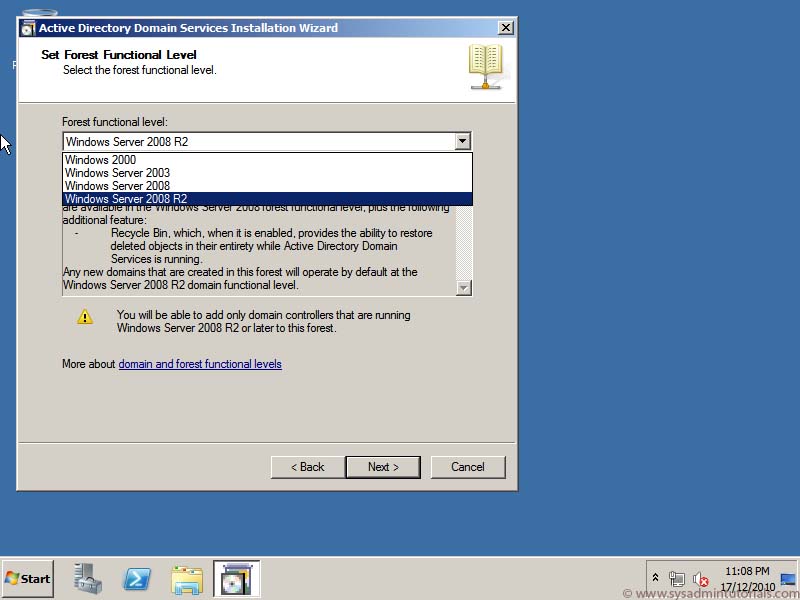
There are two ways to install Windows 2012 DCs to an existing domain as shown:
1) Perform an in-place upgrade of an existing domain controller is not recommended 2) Install a new Windows 2012 Server domain controller.Notes:
– Domain Controllers that running Windows Server 2008 or 2008 R2 can be upgraded to Windows 2012 Domain Controllers. You can upgrade a Windows 2008 DC to a comparable Ver. of Windows 2012.
– If you are running a Domain Controller based on Windows 2008 Standard or Enterprise edition you can upgrade to Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacentre edition. If you are upgrading from Datacentre edition you can only upgrade to Windows Server 2012 Datacentre edition. So if you’re running 2008 and if you’re running Windows 2003 Domain Controllers you must upgraded to Windows 2008 as an interim step, then upgraded to Windows Server 2012.
– the Forest and the Domain functional level must be Windows 2003 or higher.
– Before install the new Windows 2012 Domain Controller, or attempting to perform an in-place upgrade of an existing Windows 2008 or 2008 R2 DC, you must make sure that the Schema is upgraded to support your new Windows 2012 DC, to do this we can do it automatically within the promotion of the first 2010 domain controller or youcan be run it separately by use the ADPREP.exe tool found in the support\adprep folder on your installation media of windows 2012 and run the two ADPREP.exe commands as shown:
ADPREP.exe /forestprep (to prepare the Schema) and ADPREP.EXE /DOMAINPREP /GPPREP (to prepare each domain).
In order to run ADPREP.exe /forestprep and ADPREP.exe /domainprep /gpprep you need to be a member of the following groups:
- Scheme Admins
- Enterprise Admins
- Domain Admins
Install a new Windows 2012 Server domain controller:
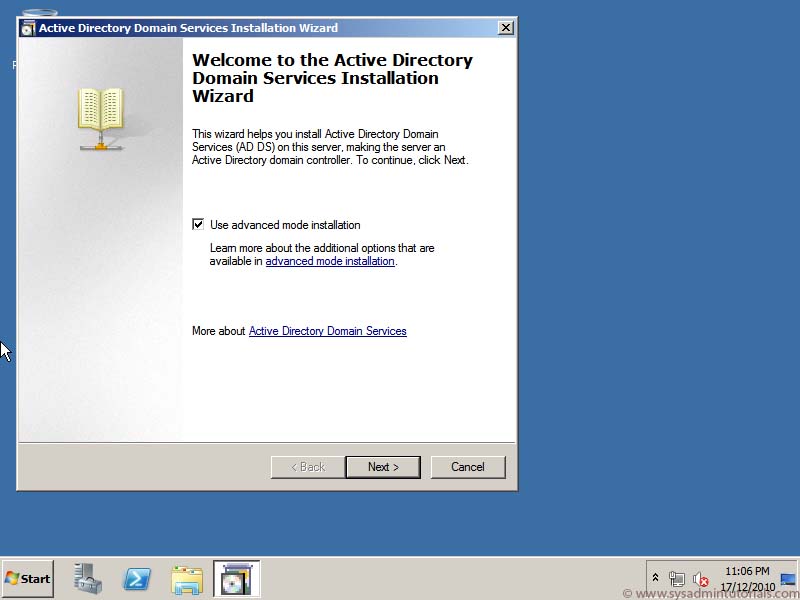
Promoting the Domain Controller DCPROMO is deprecated beginning with Windows Server 2012. Instead you will use the Active Directory Domain Services configuration wizard. Say that 10 times fast! After installing the AD DS Role, you will use either a separate wizard within Server Manager, or using the ADDSDeployment PowerShell module to promote your Domain Controller.AD DS Role Installation:
- In Server Manager, click Manage and click Add Roles and Features to start the Add Roles Wizard.
- On the Before you begin page, click Next.
-
On the Select destination server page, click Select a server from the server pool, click the name of the server where you want to install AD DS and then click Next.
-
On the Select server roles page and select Active Directory Domain Services then on the Add Roles and Features Wizard dialog box, click Add Features then click Next.
-
On the Select features page, select any additional features you want to install and click Next.
-
On the Active Directory Domain Services page, review the information and then click Next.
-
On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
-
On the Results page, verify that the installation succeeded, and click Promote this server to a domain controller to start the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard.
Promote to Domain Controller:
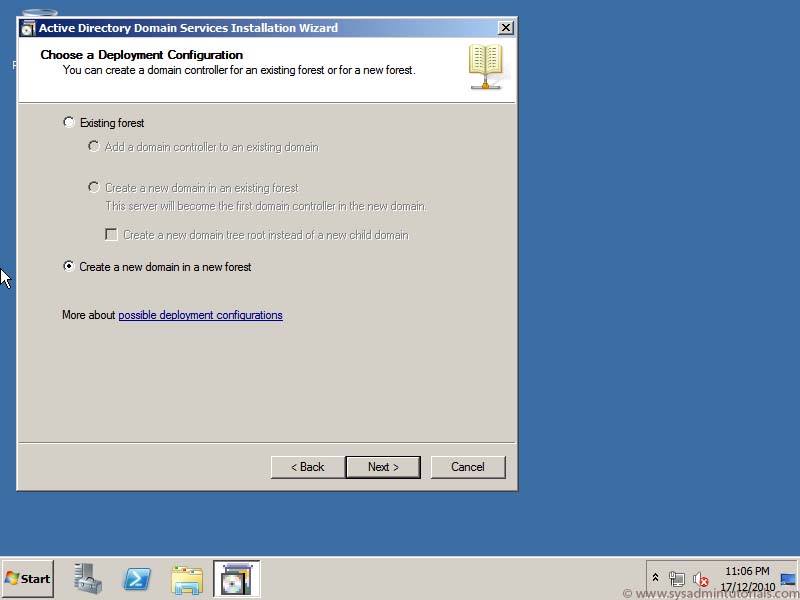
1. On the Deployment Configuration page, you have three choices.
- Add a domain controller to an existing domain
- Add a new domain to an existing forest
- Add a new forest
Since we are just adding a 2012 Domain Controller to our environment, we will select the first option.
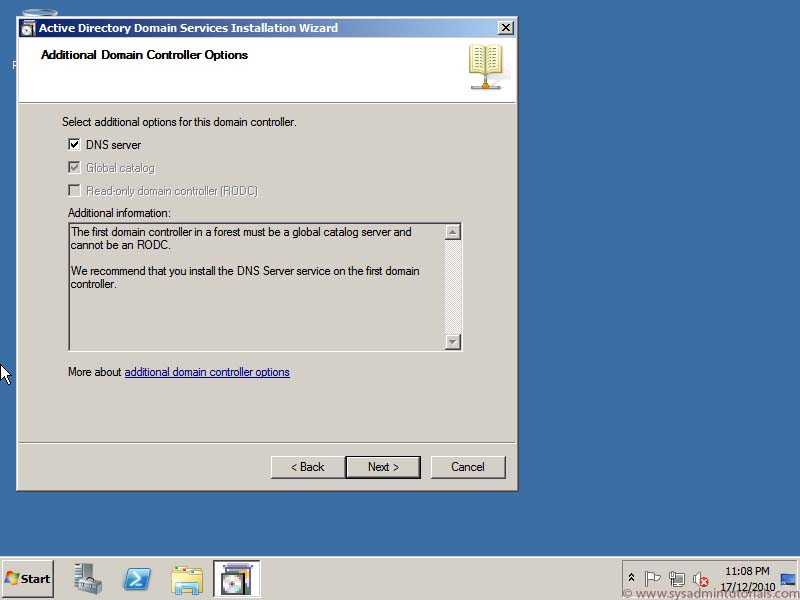
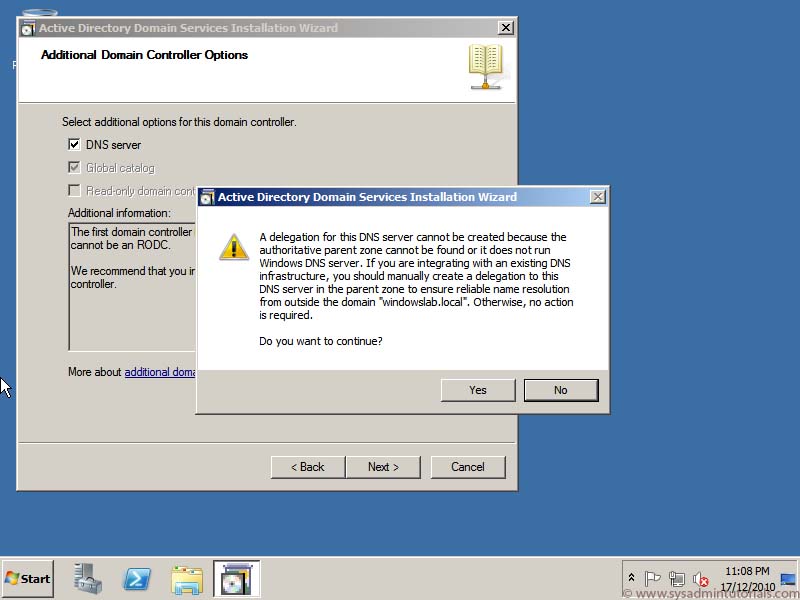
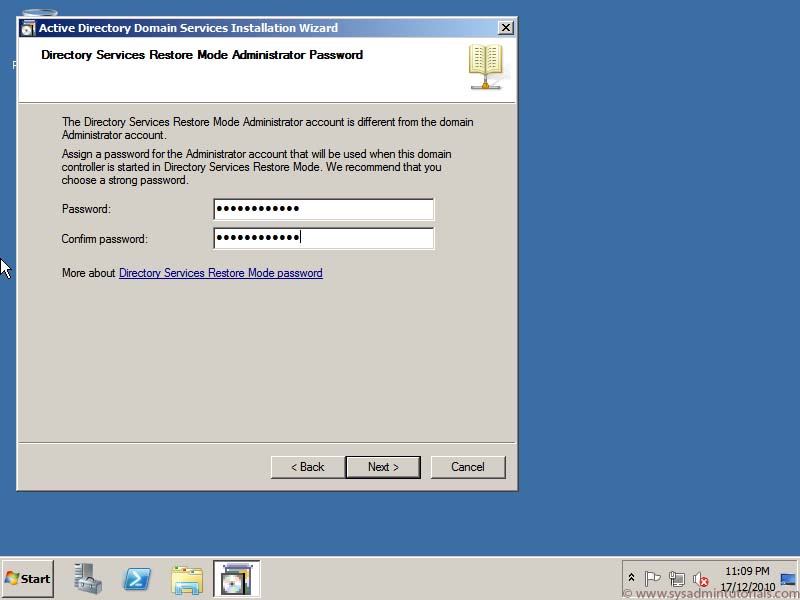
2. Click Domain Name System (DNS) server, Global Catalog (GC), or Read Only Domain Controller (RODC) as needed, choose the site name, and type the DSRM password and then click Next.
3. Select the domain controller that you want to replicate the AD DS installation data from (or allow the wizard to select any domain controller).
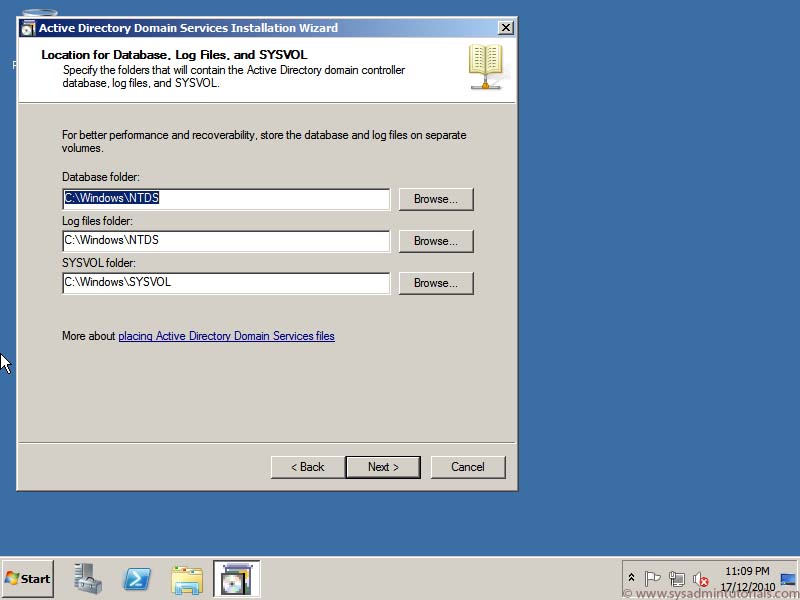
4. On the Paths page, type the locations for the Active Directory database, log files, and SYSVOL folder (or accept default locations), and click Next.
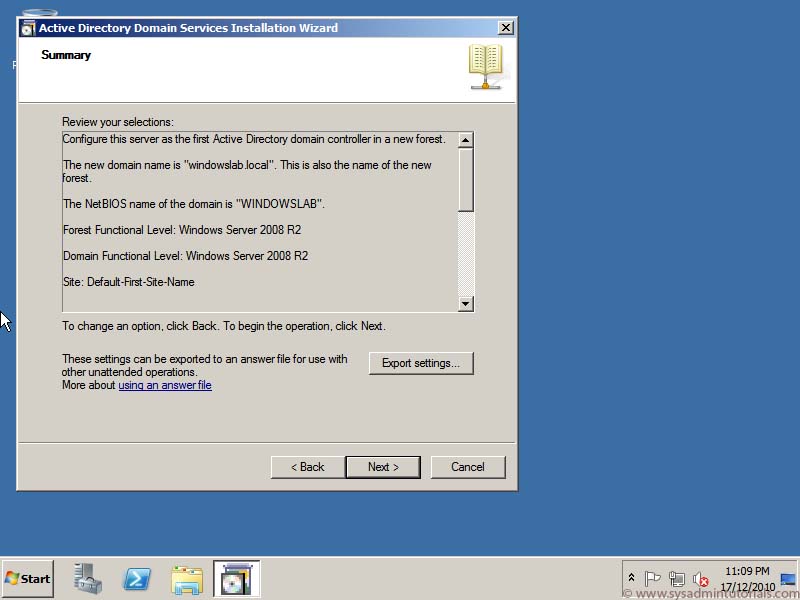
5. On the Review Options page confirm your selections, and click Next.
6. The Prerequisites Check is a new feature in AD DS 2012 domain configuration. This new phase validates that the server configuration is capable of supporting a new AD DS forest. These checks will alert you with suggested repair options. The Checks will also inform you of new security changes that will affect older operating systems.
On the Prerequisites Check page, confirm that prerequisite validation completed and then click Install.
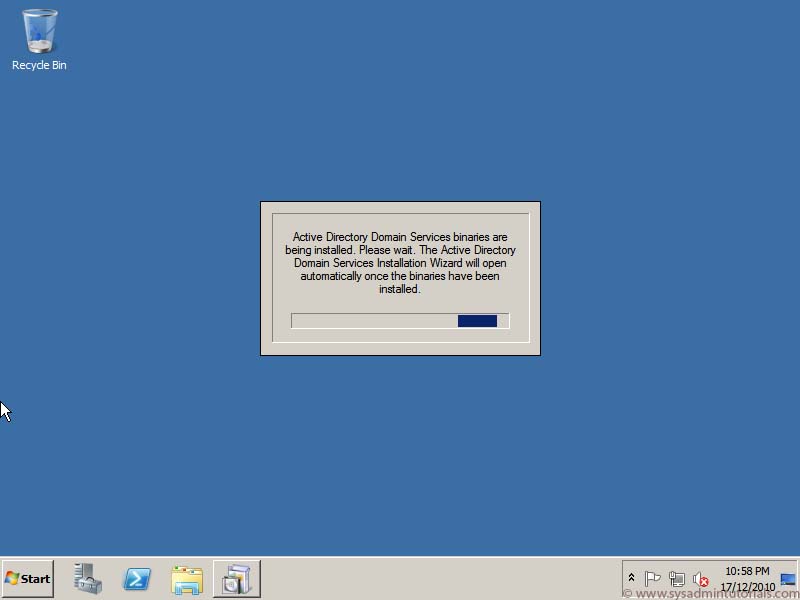
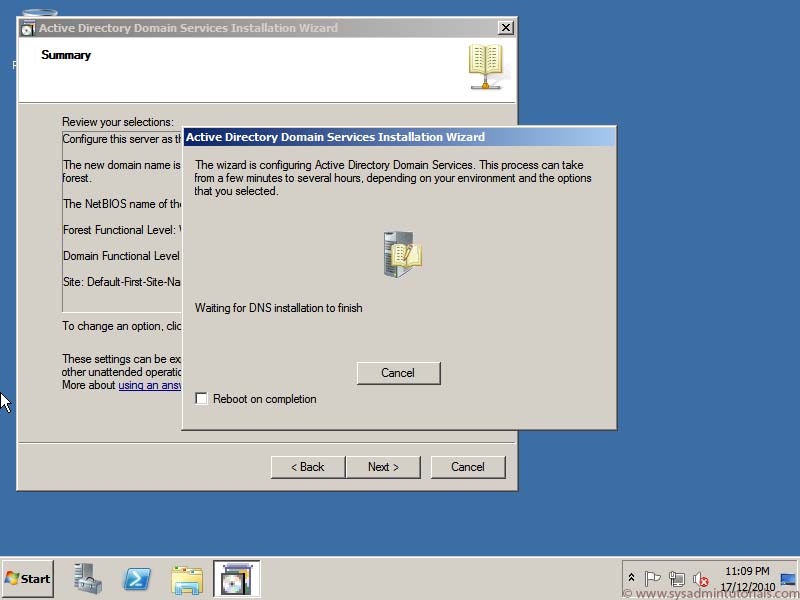
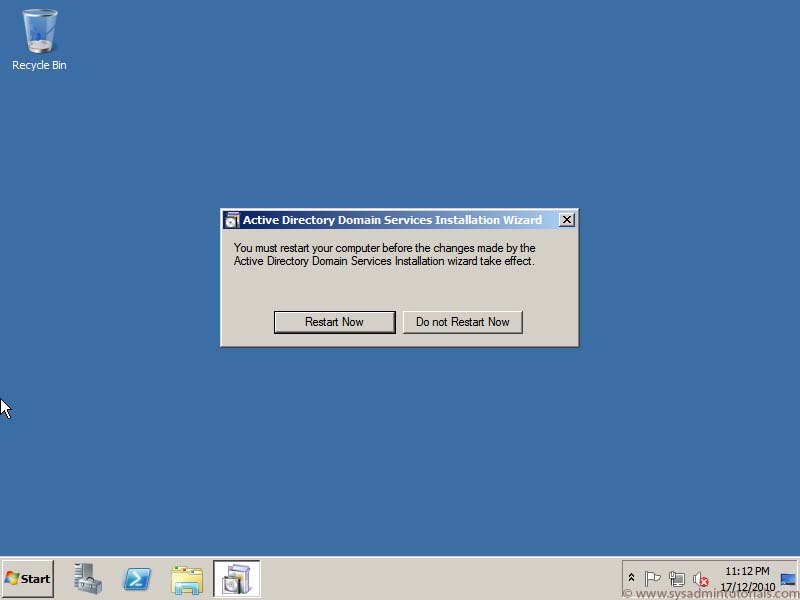
7. Clicking install will begin the domain controller promotion process. This is the last opportunity to cancel the entire installation. After it starts, there is no going back. The server will reboot automatically at the end of the promotion. The server will write two logs during the promotion. You can check them at the following locations.
- %systemroot%\debug\dcpromo.log
- %systemroot%\debug\dcpromoui.log
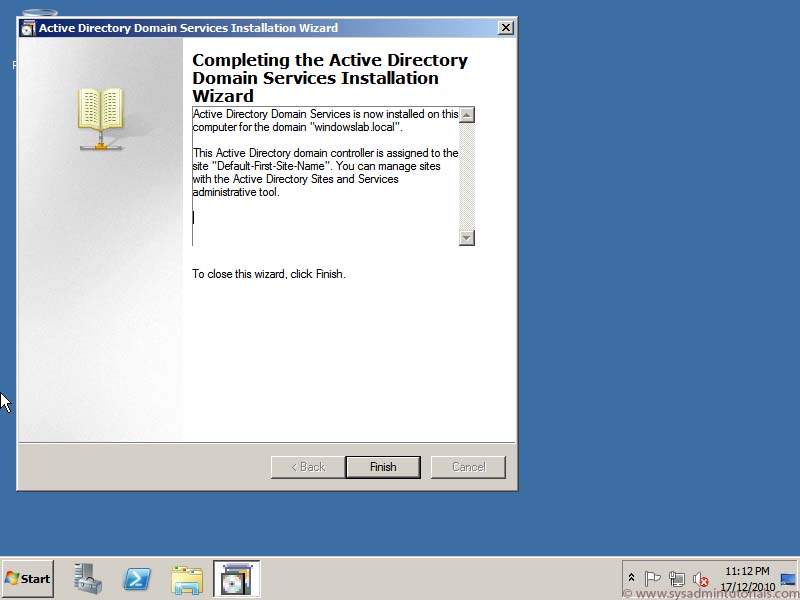
You now have a Windows 2012 Domain Controller in your environment.
Posted by Hassan Mahdy | Filed under Active Directory, Deployments